April Security Updates: Critically Patching Windows, Flash Player, and Shockwave Player
As usual for Patch Tuesday, many security updates were issued. I’m here to provide all the details for these critical updates. Not only did Windows get patched, but Adobe Flash and Shockwave Players did too.
Microsoft released a span of nine patch bundles, plugging security holes in Windows and other products. Separately, Adobe did its usual thing, and took part in Patch Tuesday as well for updates to Adobe Flash and Shockwave Players.
A cumulative update was made to Internet Explorer, which fixed two critical vulnerabilities present in almost all versions of Internet Explorer (in history). It should be noted that this includes IE 9 and 10.
There were many other updates for Windows worth noting.
Either you will receive Automatic Updates, if you’ve set Windows up to do so. Otherwise, go to Start, search Windows Update. Or for Windows 8, search for Windows Update on the Start screen.
Other than that, Adobe brings an update to Adobe Flash Player for Windows and Mac to v. 11.7.700.169. Linux should be updated to 11.2.202.280. Android 4.x+: 11.1.115.54 and 2.x-3.x: 11.1.111.50.
Keep in mind that Google Chrome and Internet Explorer 10 (Windows 8) automatically update Flash Player on their own.
Shockwave Player should be updated as well to v. 12.0.0.122! For these updates, go to www.Adobe.com
You should be able to update to Adobe AIR, which will help secure your computer even further from vulnerability. If you have Adobe AIR installed, which is required for quite a few programs that are built on its architecture (such as Tweetdeck, Pandora Internet Radio, games, etc.). AIR should automatically prompt to update.
Urgent Security Fixes Issued for Windows, Adobe Flash Player & AIR

Windows
The usual round of updates are in. As today is Patch Tuesday, Windows and Adobe Flash and Air were issued security updates. Microsoft had seven update bundles containing 20 total vulnerabilities in Windows and other Windows software. Adobe released updates for Flash and Air.
Microsoft had four critical patches, and three other updates. A total of seven today.
The critical patches address bugs in Windows, Internet Explorer, Microsoft Silverlight, Microsoft Office and Microsoft SharePoint. Updates are available for Windows XP, Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows Server 2003, 2008 and 2012.
Either you will receive Automatic Updates, if you’ve set Windows up to do so. Otherwise, go to Start, search Windows Update. Or for Windows 8, search for Windows Update on the Start screen.
Adobe Flash Player/AIR
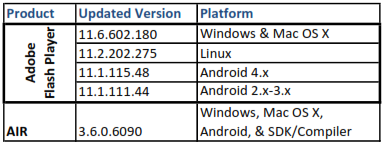
Adobe has sent updates for Flash Player, now at 11.6.602.180. This is the version for Windows and Mac OS X based systems. Four security flaws were identified, which prompted this fix. No current attacks/exploits have been identified.
Keep in mind that Google Chrome and Internet Explorer 10 (Windows 8) automatically update Flash Player on their own. The update may not be issued for Chrome just yet, but should be soon, we hope.
If you have Adobe AIR installed, which is required for quite a few programs that are built on its architecture (such as Tweetdeck, Pandora Internet Radio, games, etc.). AIR should automatically prompt to update.
Here is the update table for Adobe Flash Player and AIR:
Pwn2Own (2013) Contest a Blast – FULL Results
CanSecWest is a conference, and 2013’s conference once again involved the Pwn2Own contest for hackers, an elite (1337) competition. The concept remained simple and will always that if you pwn a fully-patched browser running on a fully-patched laptop, you get to keep the laptop.
However, different rules applied this year. It involved successfully demonstrating the exploit, providing the sponsor (HP) the fully functioning exploit, and all details involved with the vulnerability used in the attack. If there were many vulnerabilities, multiple reports are needed, etc.
The work couldn’t be sold to anyone else, and proof of concept would belong to HP once sold. Basically, HP buys the winning exploits for own use. Their idea of reward money was the following:
- Google Chrome on Windows 7 = $100,000
- IE10 on Windows 8 = $100,000 or IE9 on Windows 7 = $75,000.
- Mozilla Firefox on Windows 7 = $60,000
- Apple Safari on Mac OS X Mountain Lion = $65,000
- Adobe Reader XI and Flash Player = $70,000
- Oracle Java = $20,000
It was assuredly a blast at the competition, no doubt about it.
DAY ONE: Java, Chrome, IE10, and Firefox PWNED!!!
(Where’s Safari, right? It survived!)
The idea behind each attack is the ability to browse to an untrusted website where you’re able to inject and run arbitrary code outside of the browsing environment.
Of course, one of the rules is: “A successful attack … must require little or no user interaction and must demonstrate code execution… If a sandbox is present, a full sandbox escape is required to win.”
 In addition to Chrome, Firefox, and IE10 being pwned, Java was pwned three times on the first day. Once by James Forshaw, Joshua Drake, and VUPEN Security. VUPEN Security also led a lot of the pack of issues by successfully exploiting IE10 and Firefox as well.
In addition to Chrome, Firefox, and IE10 being pwned, Java was pwned three times on the first day. Once by James Forshaw, Joshua Drake, and VUPEN Security. VUPEN Security also led a lot of the pack of issues by successfully exploiting IE10 and Firefox as well.
The only other exploit was by Nils & Jon, where both successfully exploited Chrome.
The day after the first day of Pwn2Own, Mozilla and Google patched the exploits that were pushed out. Amazingly fast, Firefox went on to version 19.0.2 (which you should’ve been updated automatically), and Chrome went on to version 25.0.1364.160 (effectively patching 10 vulnerabilities).
“We received the technical details on Wednesday evening and within less than 24 hours diagnosed the issue, built a patch, validated the fix and the resulting builds, and deployed the patch to users,” said Michael Coates, Mozilla’s director of security assurance, in a Thursday blog.
Microsoft has decided to wait until next week’s Patch Tuesday run of updates to push out the fix for the Internet Explorer exploit on IE10.
DAY TWO: Adobe Reader and Flash Player PWNED!!! Java PWNED AGAIN!!!
The last day of Pwn2Own 2013 went with a BANG!
Flash Player…exploited by VUPEN Security (any surprise?). Adobe Reader PWNED by George Hotz. Java once again was exploited, this time proxied by Ben Murphy.
Who’re the overall prize winners?
- James Forshaw, Ben Murphy, and Joshua Drake for Java – each $20,000
- VUPEN Security for IE10 + Firefox + Java + Flash – $250,000
- Nils & Jon for Google Chrome – $100,000
- George Hotz for Adobe Reader – $70,000
Of course, George Hotz is best known for jailbreaking the iPhone and PlayStation 3. He’s still in progress with a lawsuit with Sony over the issue for PS3.
It’s amazing to see that Java was PWNED 4 times in just two days, but is it any surprise based on the number of vulnerabilities Oracle has dealt with for Java?
Now in its eighth year, Pwn2Own contest had $480,000 in payouts, a record year. Amazing!
Got any vibe on this issue? Post comment below! 🙂
Adobe Flash Player Critically Affected Again! Two Bugs Resolved!
Adobe has published another update now, fixing three vulnerabilities. Two of these three vulnerabilities are currently being exploited in the wild.
Adobe has introduced the Flash Player sandbox a year ago protecting Firefox users from vulnerabilities in Flash Player. This sandbox is being actively targeted for attacks.
“Adobe is aware of reports that CVE-2013-0643 and CVE 2013-0648 are being exploited in the wild in targeted attacks designed to trick the user into clicking a link which directs to a website serving malicious Flash (SWF) content,” the company wrote in a security bulletin.
Adobe classifies the update at priority rating of 1 for Windows and Mac (which means super-critical: PATCH NOW!), and 3 for Linux (not as critical for Linux).
Google automatically patches for Chrome Browser. Microsoft automatically patches for Internet Explorer 10 for Windows 8 (note for Internet Explorer 10 for Windows 7, you have to patch).
The following issues are resolved:
- Permissions issue with the Flash Player Firefox sandbox (CVE-2013-0643)
- ExternalInterface ActionScript feature (CVE-2013-0648)
- Buffer overflow in Flash Player broker service (CVE-2013-0504).
Update link for Windows and Mac
Update link for all other versions
To see version information about Flash Player or what browser/OS you’re running, check out the following.
Remember, when updating, UNCHECK McAfee | Security Scan Plus, unless you really want to scan your computer. It is pre-checked, so you have to uncheck it.
Two Zero-Day Bugs Found in Adobe Flash Player; Fixed with Update
Recently, two zero-day vulnerabilities were found in Adobe Flash Player, in which Adobe – today, issued an emergency update to solve. Adobe said in its advisory over the issue that one of the vulnerabilities, CVE-2013-0634, is being exploited in the wild.
The currently exploited vulnerability is being delivered as an attack via malicious Flash content, which is hosted on sites that target Flash Player in Firefox or Safari on the Mac OS platform. There are also attacks found for Windows users that trick users into opening a Microsoft Word document delivered as an email attachment. No surprise?
The second flaw, CVE-2013-0633, is being exploited in the wild in targeted attacks, doing the same with malicious Microsoft Word documents being implanted in email attachments.
Updates are available for the following platforms:
- Windows, 11.5.502.149, download
- Macintosh, 11.5.502.149, download
- Linux, 11.2.202.262, download
- Android 4.x, 11.1.115.37, download
- Android 2.x-3.x, 11.1.111.32, download
- Google Chrome, 11.5.31.139, automatic update
- Internet Explorer 10, Windows 8, 11.3.379.14, automatic update
To see version information about Flash Player or what browser/OS you’re running, check out the following.
Remember, when updating, UNCHECK McAfee | Security Scan Plus, unless you really want to scan your computer. It is pre-checked, so you have to uncheck it.
Get protection from vulnerabilities now:
Adobe Issues Critical Security Updates for Flash and AIR
Election Day brings Adobe’s critical updates for Flash and AIR, so update today to fix seven (7) vulnerabilities.
Updates are currently available as follows:
FLASH
- Windows & Mac – 11.5.502.110
- Linux – 11.2.202.251
- Android 4.* – 11.1.115.27
- Android 3.* & 2.* – 11.1.111.24
- Google Chrome automatically updates the Flash version built in.
AIR
- Windows, Mac, SDK for iOS and Android – 3.5.0.600
Be sure to download the Flash updates for both Internet Explorer, and then for Firefox/Safari/Opera/Other browsers.
Also, note Windows Update will help install the updates in Windows 8/IE 10, reference here
October is National Cyber Security Awareness Month
Cyber security awareness is so important, and we’re going to display a few things you should be aware of this month, for you to try to make capable changes to your personal or business security perspective. You will notice some of the information below is linked to different posts here on the blog. This should help you understand each topic better! Please don’t be afraid to use each of the links below to learn more about protecting your system(s).
- Email is one of the biggest attack methods. Since users are still highly dependent on email, it is so critical that email systems get fixed. Spam can be so cunning that it may disguise itself as your friend, someone you trust, or a bank. The main target in these spam attacks is phishing, which will allow an attacker to trick you into doing something or giving away personally identifiable information.The goal is to also download malware on to your computer, which can be used to take control of your computer and steal much more personal information. Some emails may claim to be a legitimate organization sending you an attachment, but it’s purpose is to distributed malware on your computer. It is best to secure email systems against spam. This can be done using a variety of products whether hardware or software. Make sure to secure your system(s) with the latest spam fighting utilities. Also, securing Outlook or Windows Live Mail is beneficial.
- Instant Messaging still seems to be a vector for malware attacks. Just when people drop their guard about IM security, a new band of threats affects users. Most IM attacks come in the form of spam, a message from an apparent trusted friend, or a phishing attempt/scam from a legitimate looking company. A lot of the time, when the message appears from a trusted friend, it usually means that person’s IM account or email account has been hacked and the attacker has mined the email addresses or IM addresses in order to send you these attacks. It is important to have a good Internet Security product that protects against IM attacks along with network defense.
- Exploits are the most common cause of infections on computers these days. Many of the exploits have been caused by out-of-date Java plugins or Adobe Flash Player plugins (or even fake Flash Player), among other types of plugins for your browser. Other exploits come in the form of advertisements that are catered to your interests, by the use of tracking cookies, which when you click on the ads it can lead to a site that will immediately download malware and attempt to take control of your computer.Those are just a couple of examples of why you need Internet Security protection as declared just above in the explanation for IM security. Also, having a second-opinion malware scanner can make sure that things don’t get missed, giving you maximum protection. Working on a defense-in-depth strategy for your computer can be a great way to avoid exploits.
- Downloading and installing untrusted software products is a good way to get infected with viruses, spyware, and other threats and malware. Using tools such as Web-of-Trust for your browsers is a key idea in managing whether a site is safe. Also, reading reviews for the product you are getting ready to download and purchase will help you make an informed decision. It is important to have Total Internet Security protection, as stated above in IM security. Please refer to the “Internet Security product” link for more information on securing your system(s) with protection mechanisms.
There are many more vectors of cyber security problems. It is important to use the methods described above as well to secure your system(s) from attacks from cybercriminals.
Summary of mitigating most attacks:
- Have a good antivirus or internet security product for maximum protection against malware, exploits, etc.
- Have a defense-in-depth PC strategy to help secure your system(s) against malware and exploits, among other threats.
- Keep abreast of the latest malware threats, so you know the seriousness of securing the system(s).
- Having a second-opinion malware scanner is not a bad idea to help secure even further against malware and exploits.
- Watch out for fake bank emails, so you can keep your financial information very safe!!
- Avoid digital disasters by backing up your data on to an external drive, CD/DVD, etc. Using a backup solution can mitigate this problem (especially for businesses).
- Always maintain a good password on any online account, especially social networks and banks!
Windows 8 Security Features Explained (mini-whitepaper)
Windows 8 is apparently more secure than Windows 7. Perhaps this is true, and it is best to learn what security features there are for the new operating system. Some of these security features are verified to help out very well in the security of Windows 8, and some may not be in time, or lastly some may not work at all.
One of the most discussed security features is Secure Boot. Now, Secure Boot is a Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) specified in the boot process to check cryptographic signatures of kernel-mode drivers, making sure they aren’t modified or corrupted. In other words, the boot process is now made to check if the operating system has been corrupted by malware or some other issue.
This is all part of a hardware restriction process called Hardware DRM. All non-ARM devices have the option to turn Secure Boot off, however ARM devices must keep it on. Experts state that it will be resistant to rootkits, since the MBR and BIOS cannot be accessed, unless if someone working on the computer penetrates it.
Next, Windows 8 features better built in antivirus software, with a much better improved Windows Defender. The software in Windows 8 is combined with the optional tool Microsoft Security Essentials. Now, with Windows Defender super-powered with MSE, it has much more anti-malware features.
With better anti-malware features, Internet Explorer is now made with better features as well. It has the ability to prevent zero-day exploits much greater than previous versions of Internet Explorer. With the challenges of exploiting Windows 7, there was the issue risen up again for Java and Flash Player, so hackers can gain control over the operating system. Those browser plugins are now easier to exploit than the Internet Explorer’s code.
A new application sandboxing environment called AppContainer provides the ability to run all apps in a controlled environment, where it controls how apps work. This prevents apps from disrupting the operating system. Of course, this is just supplemented by Internet Explorer’s SmartScreen filter, which prevents the download/install of known malicious software. However, Windows 8 now has SmartScreen available for any app, allowing even more prevention. Of course, this means Microsoft employees are going to increase in numbers, if they really want to keep up. Now that hackers know their new challenges, they will be relentless.
The questions are still played on whether Windows 8 will be a repeat of Vista or not. The reality of the situation, is if Windows 8 has big popularity, then the security issues will also light up big time. However, many will stick to Windows 7, so the security issues for Windows users are not close to be over. Feel free to take a look at related articles below for Symantec’s opinions, which aren’t too well on the new OS.
Added October 31, 2012: Trusted Platform Module, read more
Keep up with the latest security tips on our blog here. In addition, please donate to help us continue to write these awesome whitepapers.
Related articles
- Over Half Of Windows 8 Users Still Prefer Windows 7 (webpronews.com)
- Gates: New Windows 8 system is `very exciting’ (seattletimes.com)
- Windows 8 Security Is Not Good – Symantec (news.softpedia.com)
- UEFI and Secure Boot: The Hell I Went Through (prismdragon.wordpress.com)
FAQ: How did Sirefef or ZeroAccess Infect You?
In this frequently asked questions post, I will publish some of the questions people ask me, and then will post some answers from my expertise about Sirefef or ZeroAccess.
Q: How to protect from this atrocity?
A: 
Get the review of Malwarebytes’ Anti-Malware
Q: Are Sirefef and ZeroAccess the same thing?
A: YES! They are both the same, but names different by many antivirus companies. This is sometimes due to language translations and competitiveness.
Q: Can the ZeroAccess virus infect my flash drive?
A: I doubt that the virus could activate on the flash drive, unless you plugged it in while logged on to the infected Windows. If you’re worried about running something accidental on the flash drive, use USB Immunizer from BitDefender to disinfect it.
Q: Should my passwords be changed after the ZeroAccess infection? Is it only active ones to change?
All active passwords and even passive ones need to be changed. If you’re unsure about passive ones, then don’t set a new password based on old passwords. Go all fresh with new passwords. See more on passwords.
Q: What is Sirefef, how did it infect my computer, or when are new variants released?
Sirefef or ZeroAccess is a transitional rootkit, virus, and/or backdoor trojan. It is still being watched and studied constantly, having 2-3 new variants every two weeks. We stay abreast of all changes.
Q: How did Sirefef infect me?
Viruses or other malware get embedded in to webpages through iFrame exploits commonly, or through vulnerable plugin exploitation. For iFrame exploits, malware authors can create a small (1x1px) iFrame, which contains scripts necessary to run malware on a target machine by automatically downloading and installing malware. The vulnerable plugin problem happens when people fail to update Adobe Reader, Adobe Flash Player, Java Runtime Environment, Apple QuickTime, Mozilla Firefox, etc. Many times, malware authors use these vulnerable versions of the plugins to distribute an exploit, which can allow them to take control of a computer.
Other malware can be distributed by means of operating system and program bugs. Sometimes programs and very often, Windows, becomes vulnerable to attacks, because of certain bugs in the code.
Those whom do not have proper Internet security protection will fall victim to exploits.
Many people are being hit with Sirefef because of these exploits. I’d say 3/4 of people I’ve seen here on the forums have out-of-date plugins, inevitably leading to infection. Sirefef is one of the most prevalent and highly engaged malware coded problems in the past year.